Earthquake parameters
Motivation & Objectives
Earthquake catalogs represent a key input ingredient for the localization of seismic activity and for the quantification of recurrence rates for seismic hazard assessment. Some important progresses have been made in recent years, often based on a long term work done in different countries. Extended seismicity time-histories have been elaborated to be used as the backbone for objective and reliable estimates of these quantities. This is done by merging datasets of different nature and accuracy, i.e. geological observations, historical reports and instrumental catalogues. Although this effort is aimed at gathering the most comprehensive information on past earthquakes, there are still some large uncertainties in the determination of the characteristics of old earthquakes, and in the determination of the focal depth of recent events.
The general objective of this work package is to improve our knowledge of past earthquakes, by developing innovative methods and improving existing datasets, with a particular focus on low-to-moderate seismicity areas.
Coordination
Jessie Mayor (EDF) & Emmanuelle Nayman (EDF).
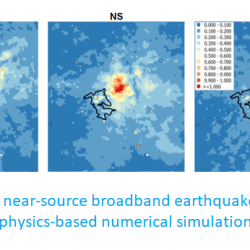
 © D. Grenié/P. Arroucau
© D. Grenié/P. Arroucau
Actions
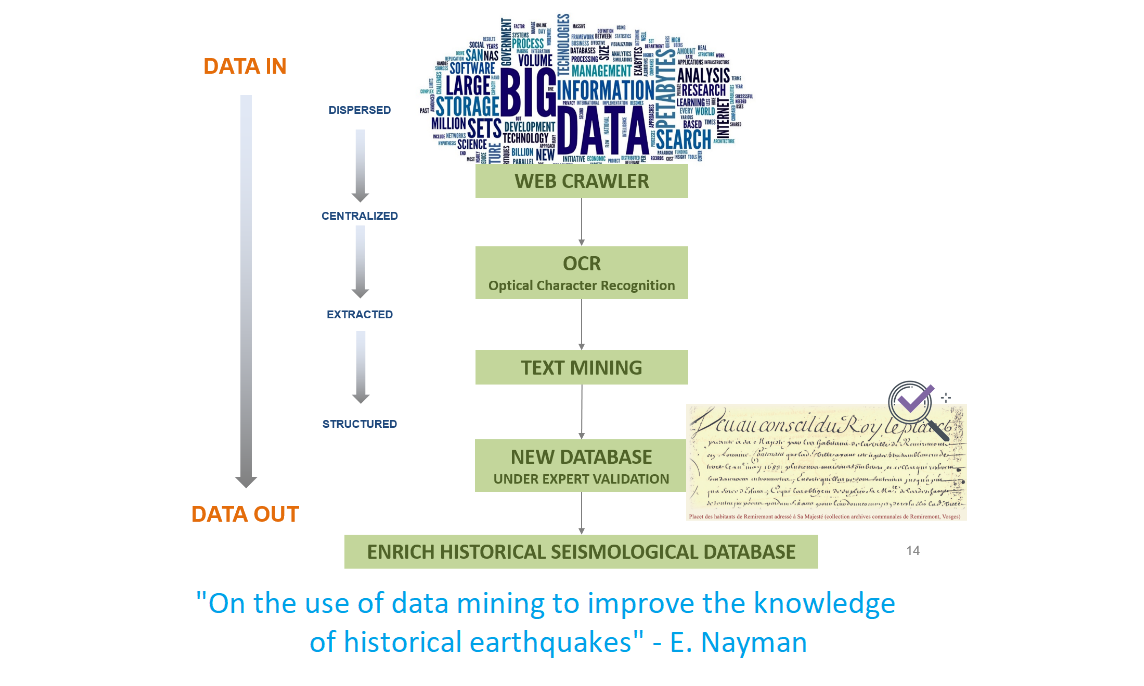
On the use of data mining to improve the knowledge of historical earthquakes
Report available! ![]() "On the use of data mining to improve the knowledge of historical earthquakes" by E. Nayman (7.94 Mo)
"On the use of data mining to improve the knowledge of historical earthquakes" by E. Nayman (7.94 Mo)
Collect additional information on historical earthquakes by deploying data-mining and text-mining approaches on the web
Motivations
In recent years growth of digital data has been increasing, and the World Wide Web (www) is the most heterogeneous and dynamic repository available. This work proposes a framework based on data mining techniques to improve knowledge of historical earthquakes by finding new records on literary heritage available on the web.
Data mining technology helps to extract useful information from various databases. Data mining on text has been designated at various times as statistical text processing, knowledge discovery in text, intelligent text analysis, or natural language processing, depending on the application and the methodology that is used ([12]).
Program of research
The method presented here focuses on a specified available corpus of documents: Gallica©, the digital library of the Bibliothèque nationale de France (BnF, [9]).The main part of this work focuses on designing methods and algorithms in order to effectively process this avalanche of text. To guarantee the success of such a process and define a precision strategy, three key steps are highlighted here:
- Exploiting existing databases: Exploiting the macroseismic database SISFRANCE (BRGM-EDF-IRSN; [7]), where about 10 000 bibliographic references have been collected to describe 6 000 earthquakes (463-2007), seismological ontology is defined and used as dedicated dictionary to extract relevant information from the Gallica© collection of documents.
- Semantic enrichment of databases and knowledge enrichment: The collection of documents are text data, which can be defined as unstructured information. Gallica© documents are semantically annotated with seismological ontology (dedicated dictionary) but also with named entities (regular expressions such as cities, dates or numbers) which constitute the knowledge base. Gallica© documents are thus turned into structured information.
- Using advanced techniques of data mining: the use of a similarity process dramatically helps to find relevant text through the background ‘noise’.
The proposed methodology aiming at finding new sources to improve past earthquake knowledge is not destined to replace historian expertise on documents themselves. Expert assessment, by analyzing and interpreting sources, and putting them into the historical context is crucial. This methodology presented here just aims at facilitating source findings and delivering new sources in their hands.
Organization
Funding member: EDF
Type: Research study
Collaboration: QWAM Content Intelligence, EDF
Status: completed

Archeoseismicity
Develop new methods for archeoseismicity
Motivations
- Explore the structural characteristics of heritage buildings.
- Understand the behavior of masonries under seismic load.
- Involve a multi-disciplinary team of archaeologists, seismologists, structural engineers and architects.
Program of research
- Develop a methodology to estimate peak ground motion from the analysis of historical buildings.
- Characterize the response of historical buildings under seismic load by combining on-field measurements, structural/architectural perspective and mechanical modelling.
- Use ambient seismic noise techniques to characterize the frequency response of selected historical buildings.
Organization
Funding member: EDF, ENS
Type: Post-doc, Internship, Research study
Collaboration: G. Poursoulis (consultant), ENS Paris-Saclay, EDF
Status: completed
Result
Report
Site effects in historical databases
Identify site effects in historical databases
Motivations
In this study, we propose to quantify and map the local site effects in Metropolitan France from the analysis of macroseismic observations. The main challenge consists here in extracting workable signatures of site-effects from a qualitative and sometimes sparse macroseismic dataset, especially in early historical times. We will use Intensity Data Point (IDP) from the SISFRANCE database (EDF-IRSN-BRGM) that covers an approximate 1000 years period up to present. In particular, we aim at extracting information over the whole territory, and to extend the analysis beyond the most seismically active areas actually covered by the instrumental catalogue.
Program of research
We aim at delivering a map of “historical site effects”. The rationale consists in searching for systematic biases in the spatial distribution of IDPs which could be related to potential local site effects. To reach this goal, we will develop two different methods: first, a grid-search approach, and second, an analysis on residuals based on a pre-selected macroseismic attenuation law.
Organization
Funding member: EDF
Type: Internship, Research study
Collaboration: EDF
Status: In progress (started 2018)
Results
Report
Magnitude and focal depth of historical earthquakes
Improve methods to estimate magnitude and hypocentral depth of historical earthquakes, especially for very incomplete sets of data
Motivations
Update the French metropolitan FCAT17 seismic catalog (output product of the preceding SIGMA project) by refining magnitude and focal depth estimates of earthquakes.
Program of research
- Complete the azimuthal-coverage of macroseismic observations
- Update inversion scheme taking into account realistic uncertainties on historical epicentral locations
- Account for the discrete character of macroseismic intensity values in the likelihood function
- Incorporate a weighting function on (M, h) pairs using a Bayesian framework
- Investigate the clustering of events based on g parameter value (Mayor et al., 2017)
Organization
Funding member: CEZ
Type: Research study
Collaboration: EDF
Status: In progress (started in 2017)
Results
Report
Revision of the Czech National Earthquake Catalogue
Report available! ![]() "Revision of the Czech National Earthquake Catalogue" by I. Prachar et al. (7.88 Mo)
"Revision of the Czech National Earthquake Catalogue" by I. Prachar et al. (7.88 Mo)
Motivations
Before the development of a Czech National Earthquake Catalogue, seismic hazard assessment studies relied on the use of personal datasets, elaborated independently by individual Czech experts. The goal of this action was to update and share a new version of the Czech catalogue with the international community of seismologists. The main scientific objective was to reduce epistemic uncertainties in earthquake locations over the Czech Republic area, and to develop collaboration so as to benefit from the FCAT-17 return-on-experience.
CZ-NEC (CZech National Earthquake Catalogue) is a scientific product which makes available data on earthquakes in the Czech Republic and in its surroundings. During the work on the catalogue, the CZ NEC team accepted the challenge to prepare an earthquake catalogue for the entire Bohemian Massif. This expansion of the area of interest has already required the invitation of seismologists and creators of earthquake catalogues from neighboring countries, especially from Austria and Germany. Due to this expansion, the work on the catalogue had to be divided into two phases.
This report contains the results of three years of work on phase I. Phase II. should follow this phase and will be built primarily on working with German colleagues.
CZ-NEC is made openly available; therefore, it will be published also on the Internet. The web presentation of the catalogue is based on the Midop and ArcGis Online software. Converting CZ NEC catalogue to the web environment will allow continuous updating and improvement of the catalogue, both in the form of adding of newly occurring events and reviewing and reassessment of historical earthquakes. The CZ NEC team has gathered a very rich archive of sources, as monastic annals, chronicles, old prints, newspaper reports and newer publications on earthquakes, which will also be made available to serious researchers interested in continuing work on the CZ NEC.
Program of research
- Digitalize the Kárník’s catalogues, which are the fundamental inputs for catalogue revision.
- Extract events (records) with epicenters on the Czech Republic territory and its close surroundings, resp. in source zones covering (also partly) the Czech Republic territory.
- Develop the instrumental part of the catalogue for earthquakes recorded since 1978.
- Revise of all catalogued events in terms of record reliability, epicentral coordinates, intensity and/or magnitude estimates, other parameters…
- Verify historical sources of information (i.e. chronicles, older catalogues, publications, newspapers, and macroseismic questionnaires) as well as instrumental records.
- Deploy a unified moment magnitude scale.
- Produce a background study describing the work methodology, used sources and instrumental records and a discussion on selected events.
- Create a web application for the sharing of the catalogue. Publish results in a peer-reviewed international scientific journal.
- Incorporate the Czech National Earthquake Catalogue update into compiled Regional Earthquake Catalogue for Temelin and Dukovany NPP regions, Czech Republic.
- Review the existing European SHEEC catalogue and eventually make recommendations for its revision.
Organization
Funding member: CEZ
Type: Research study
Collaboration: CEZ, I. Prachar (consultant), J. Pazdirkova (institute of Physics of the Earth, Brno)
Status: completed
Results
Report
A preliminary three-dimensional seismological model of the crust and uppermost mantle for Metropolitan France
Report available! ![]() "A preliminary three-dimensional seismological model of the crust and uppermost mantle for Metropolitan France" by P. Arroucau (4.75 Mo)
"A preliminary three-dimensional seismological model of the crust and uppermost mantle for Metropolitan France" by P. Arroucau (4.75 Mo)
Motivations
The motivation for this action was to gather existing information on geological provinces and boundary, and associate these results with seismological data so as to produce a 3-D crustal velocity model over the France metropolitan area. The main interest is to provide more constrained crustal velocity information for earthquake locations in metropolitan France, in particular for areas covered by a loose seismological network.
Program of research
We present a new three-dimensional (3D) seismological P- and S-wave speed model of the crust and uppermost mantle for Metropolitan France (i.e. the part of France located in Europe) and neighboring countries, primarily aimed at earthquake location. The model extends from 8°W to 13°E in longitude and 40°N to 52°N in latitude, and from the earth’s surface down to 100 km depth. It is parameterized on a regular, 10 km x 10 km x 0.5 km grid and includes two explicit interfaces: the topography/bathymetry, which we set to that of ETOPO1, and the crust-mantle boundary that we model from previously published controlled-source seismics and receiver function studies by means of a probabilistic surface reconstruction technique. The modeled Moho depths range from 14 to 54 km, which is consistent with the current tectonic setting of France that encompasses regions of thinned continental crust and thickened orogenic areas. Our reference model for P- and S-wave speeds in the crust is EPcrust (Molinari and Morelli, 2011), which we combine with recently published tomographic models by weighted average. When only P- or S-wave speed is available, the other quantity is calculated using a Vp/Vs value of 1.70, and the resulting model is assigned a lower weight than the original one. A similar weighted average model is used for the mantle, however the Vp/Vs ratio is inferred from ak135 model. Information from Pn and Sn tomography is also incorporated, with a weight decreasing from 0.5 at Moho depth to 0.0 at 60 km. The final model is accompanied with a 3D weighted standard deviation grid for both Vp and Vs, which provides a quantitative estimate of wave speed uncertainties. The resulting model shows significant deviations from a one-dimensional (1D) model, with lateral variations ranging from ~1-2 % in the mantle up to ~20% in the upper crust. This model can readily be used to produce homogeneous locations of earthquakes in Metropolitan France and neighbouring areas, although its actual potential for hypocentral solution quality improvement still needs to be assessed. This model can also be used as a starting model for local earthquake tomography or to correct for crustal effects in teleseismic tomography.
Organization
Funding member: EDF
Type: Internship, Research study
Collaboration: EDF, EOST, University of Nantes
Status: completed

Magnitude and focal depth in instrumental catalogues
Develop methods to refine instrumental magnitude and focal depth of small-magnitude events in low-to-moderate seismicity areas
Motivations
In regions of low-to-moderate seismic activity, catalogues are mainly composed of small magnitude events. This population of events can then be used, for instance, to constrain recurrence laws for seismic hazard assessment. Depending on the instrumentation used for the recording of such small-magnitude earthquakes, biases may appear in seismic moment estimates. First, inhomogeneous network coverage can cause large uncertainties or bias in focal depth estimates. Second, weak low-frequency (LF) energy radiation for small-magnitude events question the pertinence of the classical approach used for moment-magnitude estimates (Brune, 1970).
Program of research
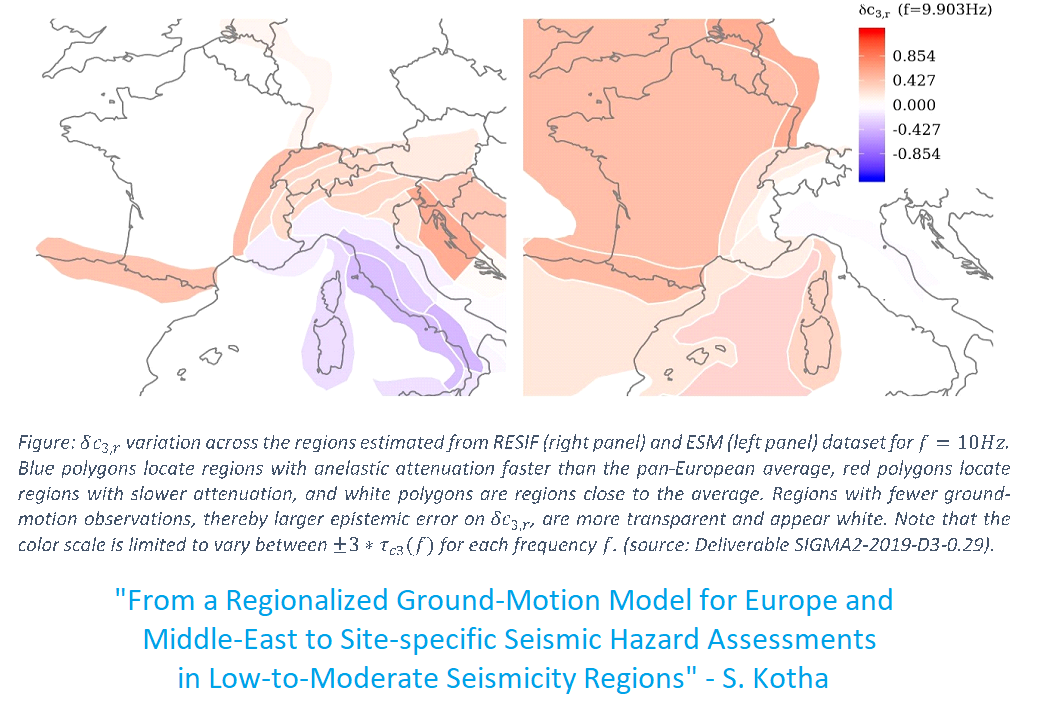
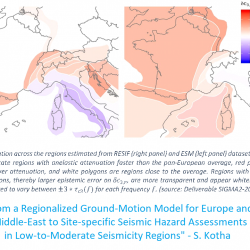
We propose to improve the methodology to estimate instrumental magnitude which is based on the quantitative modeling of the seismic energy envelop. This includes the radiation effects of the source, intrinsic attenuation and scattering. In fact, the modeling of the entire seismic envelop of the signal - direct and diffuse (or coda) waves – is the key to distinguish the source, site and propagation effects. These developments will benefit from the improved data coverage over France and from the high-quality seismic data delivered by the dense RESIF seismic network.
Organization
Funding member: EDF, CEA, Univ. Toulouse
Type: PhD project
Collaboration: EDF, CNRS/IRAP (Toulouse University), CEA (LDG)
Status: In progress (2018-2021)
Results
Report
Improve depth of instrumental earthquake locations using secondary arrivals
Motivations
In metropolitan France, during this last decade, several actions have been conducted to improve the quality of localization and characterization of the seismicity : improvement of the seismic network in the framework of RESIF with almost homogeneous coverage expected by 2020, production of a reference catalogue of seismicity for the period 1962-2009 (Si-Hex project) through collaborative work between the various actors involved in the monitoring and analysis of seismicity at the national or regional level, constructions of 3D model at regional scales, etc.
The objective of the proposed research is to pursue this effort by performing synthetic tests in realistic network configurations and seismicity distribution to better quantifie the uncertainties on earthquake location, and the possible associated bias. The goal will be to test the effect of network evolution over the period 2010-2018 integrating the stations from RESIF seismic networks and other French or foreign networks used for the seismicity analysis at BCSF-RéNaSS. Moreover, secondary phases (Pn and Sn) are routinely used for the earthquake location at the national scale (BCSF-RéNaSS), the Post-doc fellow will also explore the effect of using Pn/Sn in presence of Moho depth uncertainties, and more generally effect of 3D vs 1D velocity model.
Program of research
To carry out this task, direct, global-search location algorithms which are not affected by errors due to nonlinearity of the inverse problem will be used, integrating secondary phases. The influence of other depth or secondary phases (e.g. PmP, sPn, etc) may also be explored. This work would benefit from another work done in the SIGMA2-WP2 project aiming at building a 3D Earth model at the scale of the metropolitan France (action 2.6).
Organization
Funding member: EDF
Type: Post-Doc
Collaboration: EOST, University of Strasburg
Status: not started yet
Results
Report